It is amazing to see how technology can improve the learning of our students. I have introduced gamification in my classroom at EM Normandie Dublin Campus, and it has increased students’ engagement significantly. More details : Click here
Scales4Research Scholar GPT by Professor Rajibul Hasan
Introducing the Scales4Research Scholar GPT, which is more than just a tool; it’s a gateway to a new era in research within Business, Innovation, Marketing, and Psychology. By simplifying and refining the process of scale development, this tool not only aids researchers in creating more accurate and reliable scales but also contributes to the advancement of knowledge in these critical fields. It’s a testament to how targeted technological solutions can have far-reaching impacts in the realm of academic research.
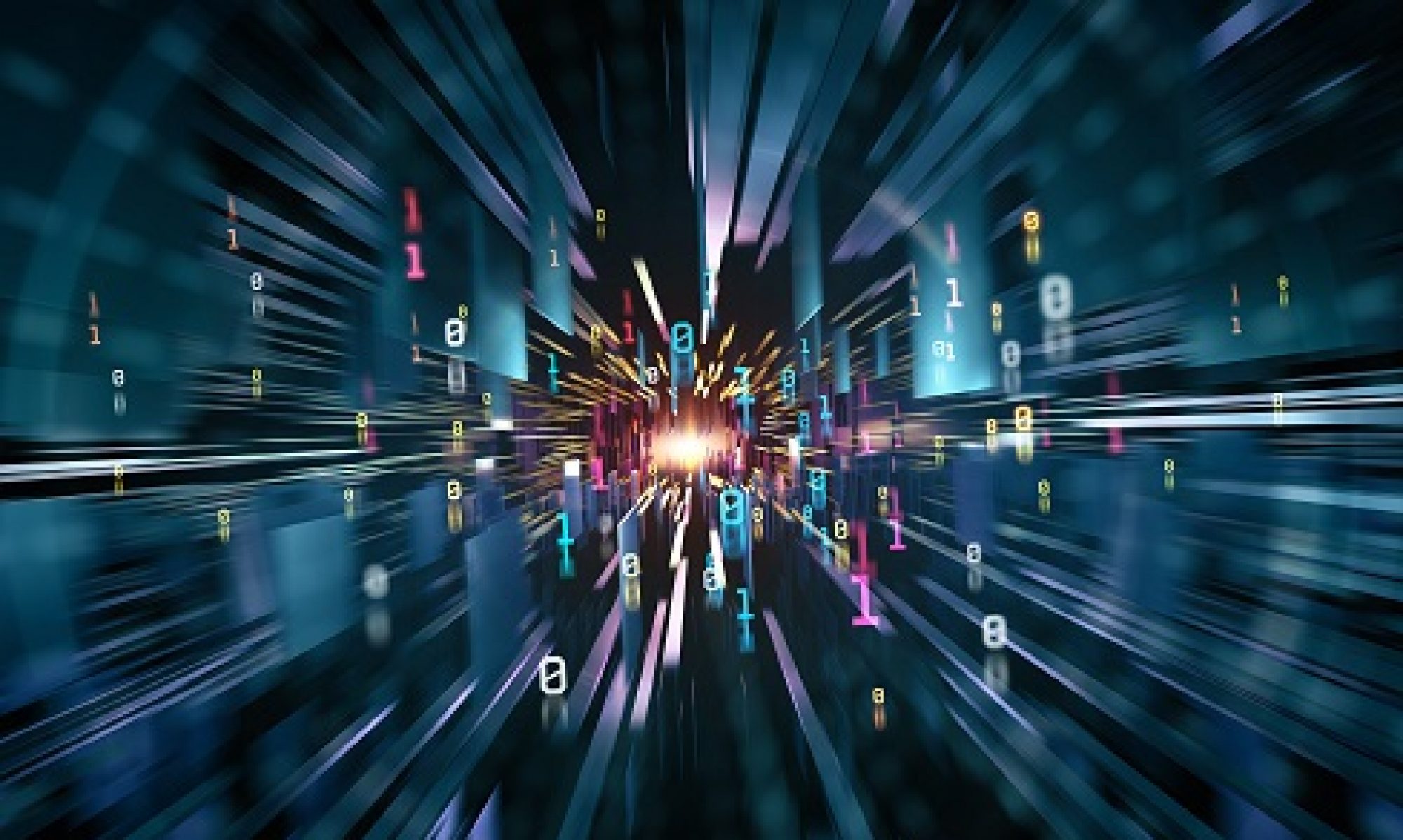
Unlocking the Future of Community: Exploring the Perceived Value of SIoT-Based Online Communities in Smart Kitchens- New Research Article by Professor Dr Rajibul Hasan
I am happy to share the latest article, “Consumers’ perceived value of Social IoT based online community: investigating social awareness processes surrounding smart kitchen robot appliances,” which delves into the captivating world of the Social Internet of Things (SIoT).
Situated within the broader SIoT paradigm, this research explores how smart kitchen robot appliances, like Cookeo by Moulinex, play a pivotal role in fostering online communities. The study focuses on the experiences of 335 female respondents from France who own and use SIoT kitchen robot devices.
Key findings from the research highlight that the perceived value of SIoT-based online communities is intricately linked to three essential activities within these communities: mutual aid, participation, and enjoyment. These activities, in turn, are motivated by the willingness to co-produce, connect with others, and learn from the community. This dynamic interaction showcases how SIoT technology has reshaped the meaning and historical significance of cooking as a cultural practice.
Furthermore, this research underscores the importance of gender in SIoT technology and services development, opening up critical avenues for debate and discussion.
The study’s use of Partial Least Square Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) provides a robust foundation for its conclusions, making it a valuable addition to the SIoT literature.
Article link: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0144929X.2023.2270713

A new Research Article by Professor Dr Rajibul Hasan related to SIoT robots and consumer experiences in retail
Good news! I am happy to share that our research paper has been accepted in the field of Service Robotics and Internet of Things (SIoT) at the intersection of Consumer Behavior and Retail Service! 🤖🛒 Thanks to my co-authors for their wonderful contributions.
We looked into the world of SIoT in depth, thinking about service robots and using the CASA paradigm to find out what makes customers want to buy from a business again when SIoT relationships are formed in retail services.
Embedded in Computers are Social Actors (CASA) paradigm, we leverage a Partial Least Approach – Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) (n = 356) to show that word of mouth, consumer promotion experience, relationship quality, and inspiration significantly impact consumers’ repeat purchase intention when SIoT robots are used. Noticeably, while relationship quality is significant, it has a negative coefficient indicating that consumers may have high pre-existing anxiety towards SIoT service robots.
Full article access link: SIoT robots and consumer experiences in retail: Unpacking repeat purchase intention drivers leveraging computers are social actors (CASA) paradigm – ScienceDirect

Exploring the Epistemic Value of Food Recommender Systems: A Study on Yuka’s Perceived Value
Excellent news! Our most recent publication examines Food Recommendation Systems (RecSys) and their influence on consumer food selections. Recommendation Systems’ epistemic value, particularly in relation to culinary choices, must be comprehended in today’s technologically advanced society. Our study proposes a model that establishes a positive relationship between the epistemic value and the perceived value of the Yuka company’s food Recommendation Systems. This model emphasizes the significance of compatibility, self-assurance, consumer innovation, memory, and learning. It also emphasizes the need for developers, retailers, food manufacturers, and policymakers to collaborate in order to map and adjust information through consumers’ socialised Recommendation Systems usage to shape the design of the next-generation Recommendation Systems.
To access the full article please visit- https://www.tandfonline.com/eprint/QN4XSP4NHVFZRXPSB4FN/full?target=10.1080/0144929X.2023.2212088
Exploring Tourists’ Virtual Reality-Based Brand Engagement: A Uses-and-Gratifications Perspective
Happy to share that our paper (Titled: Exploring Tourists’ Virtual Reality-Based Brand Engagement: A Uses-and-Gratifications Perspective) has been published online in the Journal of Travel Research (ABS 4). In our research, we explored the impact of tourists’ VR involvement and identification on their VR-based brand engagement and its effect on VR-based brand co-creation and loyalty intent. Our findings highlight the mediating role of VR-based brand engagement and the moderating role of tourists’ technology readiness. With VR-based brand engagement becoming increasingly important in the tourism industry, our research provides valuable insights for both academics and practitioners.
You can access the full paper by clicking the following link-
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00472875231166598
Paper citation: Rather, R. A., Hollebeek, L. D., Loureiro, S. M. C., Khan, I., & Hasan, R. (2023). Exploring Tourists’ Virtual Reality-Based Brand Engagement: A Uses-and-Gratifications Perspective. Journal of Travel Research, 0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/00472875231166598
How our ABS 4 Ranked Publication Unveils Tourists’ Virtual Reality-Based Brand Engagement and Its Implications for the Tourism Industry (Impact Factor 8.933)
Exciting news! Our paper on Virtual Reality-Based Brand Engagement has been accepted for publication in the prestigious Journal of Travel Research (ABS 4- Impact Factor 8.933). This marks my second ABS 4-ranked publication and I couldn’t be prouder of my team’s hard work. In our research, we explored the impact of tourists’ VR involvement and identification on their VR-based brand engagement and its effect on VR-based brand co-creation and loyalty intent. Our findings highlight the mediating role of VR-based brand engagement and the moderating role of tourists’ technology readiness. With VR-based brand engagement becoming increasingly important in the tourism industry, our research provides valuable insights for both academics and practitioners. Stay tuned for the forthcoming publication!
Paper citation: Rather, Raouf; Hollebeek, Linda; Loureiro, Sandra; Khan, Imran; Hasan, Rajibul(2022) Exploring Tourists’ Virtual Reality-Based Brand Engagement: A Uses-and-Gratifications Perspective. Journal of Travel Research, forthcoming.
Exploring the Impact of COVID-19 Research: A Study of Dr. Hasan’s Work in the World Health Organization (WHO) Database
Dr. Hasan’s article related to Covid-19 was also listed in the World Health Organization Data Base (https://search.bvsalud.org/global-literature-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/) and it shows the relevance and impact of his research.
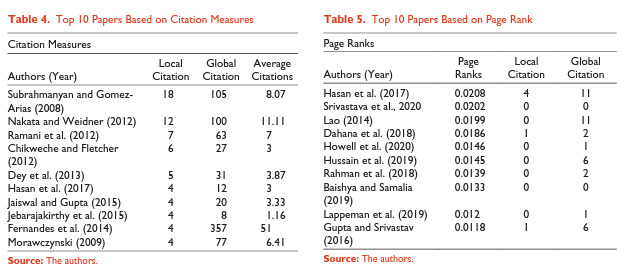
Dr. Hasan’s Paper Ranks Among the Top Ten in Page Rank and Citation Measures in Bibliometric and Content Analysis
Dr. Hasan’s paper has been identified among the top ten lists based on page rank and citation measures, according to the following research paper:
Goel, P., Sharma, N., & Saha, R. (2022). Consumption Behaviour of Poor Consumers: A Bibliometric and Content Analysis. FIIB Business Review, 23197145221115794.
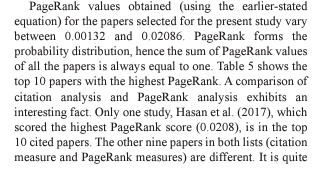
According to Goel et al. (2022), “Only one study, Hasan et al. (2017), which scored the highest PageRank score (0.0208), is in the top 10 cited papers.”

Our new research article Titled “Motives for posting fake reviews: Evidence from a cross-cultural comparison” available for a limited time period

https://authors.elsevier.com/c/1fvGpXj-jc4Iq
Related youtube video is available at:
